Rising concerns about Ocean Acidification and Warming in the Mediterranean Sea – Executive summary of the MedSeA project
This fact sheet has been compiled as part of the European project Mediterranean Sea Acidification in a changing climate (MedSeA). It is intended to aid scientists, science communicators, and science policy advisors. The MedSeA project included more than 100 scientists from 22 institutions in 12 countries…
New version available in English; previous version available in Spanish and Catalan
10 Facts on ocean acidification and Warming in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) and heat. CO2 from fossil fuel burning heats the atmosphere and dissolves in seawater. Although the absorption of atmospheric CO2 by the ocean helps limit climate warming, it also changes seawater chemistry and causes ocean acidification.
Available in English and French.
Tipping the balance: CO2 and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Reference User Group (MRUG) is an advisory body of the MedSeA project. It is composed of scientists, marine and coastal managers, conservation practitioners, industry representatives, science policy advisors and policy makers, and other stakeholders, mainly from countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. The MRUG ensures the work and results of the MedSeA project are not only promoted and widely disseminated but are translated into a form that all audiences can understand…
Available in English, Spanish, French and Arabic.
MedSeA leaflets
The ocean plays an important role in providing humans with nutrition, social and economic activities. It also acts as a carbon sink – absorbing about 30% of atmospheric CO2 released from human activities such as burning fossil fuels…
Available in English, Spanish, French, Arabic, Italian and Greek.
MedSeA scientific poster
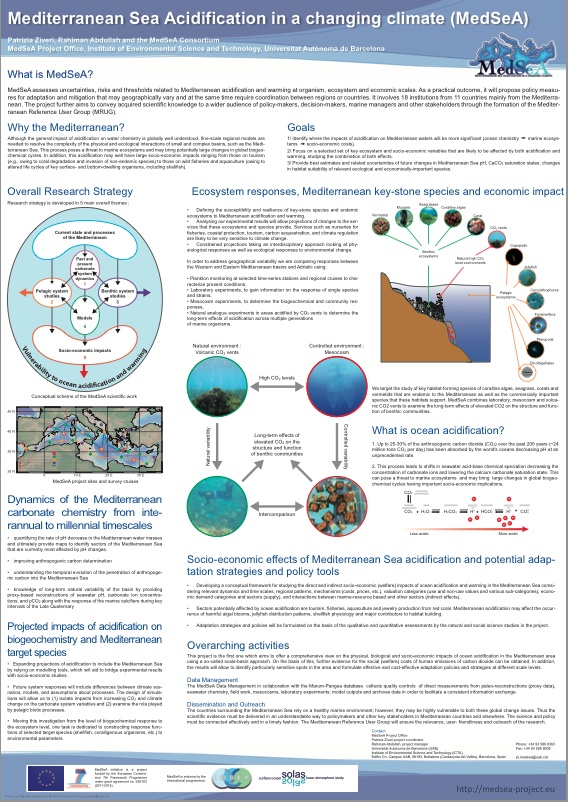
MedSeA assesses uncertainties, risks and thresholds related to Mediterranean acidification and warming at organism, ecosystem and economic scales. As a practical outcome, it will propose policy measures for adaptation and mitigation that may geographically vary and at the same time require coordination between regions or countries…
Message for Rio+20 – Ocean Acidification: Acting on evidence
This briefing paper from the International Ocean Acidification Reference User Group provides essential information and highlights the actions needed on ocean acidification by Governments at Rio+20…
Hot, Sour and Breathless: Ocean under stress
The ocean covers nearly three quarters of the Earth’s surface, contains 96% of its living space, provides around half of the oxygen we breathe and is an increasing source of protein for a rapidly growing world population. However, human activity is having an impact on this precious resource on local, regional and global scales.
Ocean Acidification: The Knowledge Base 2012 (English version)
Acidification des Océans: L’état des connaissances en 2012 (French version)
Acidificación Oceánica: La base del conocimiento 2012 (Spanish version)
Ozeanversauerung: Die Wissendatenbank 2012 (German version)
Acidificaçao Ocêanica: O conhecimento de base 2012 (Portuguese version)
FAQ on Ocean Acidification
English version
FAQ sur l’acidification des océans
French version